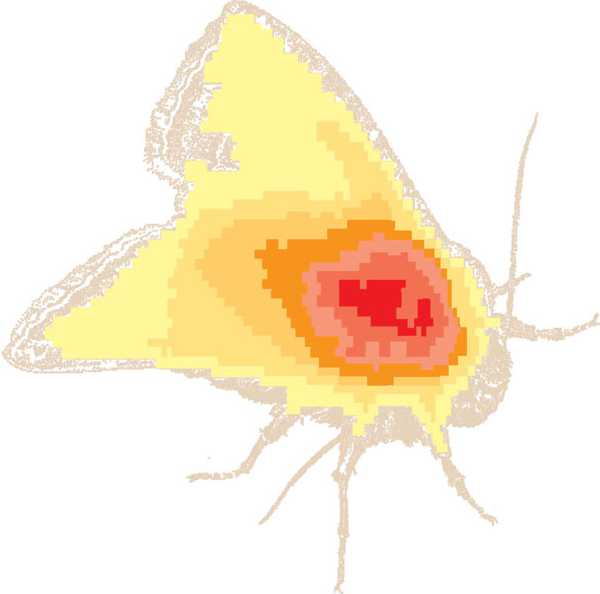
 Internal temperature in the winter moth.
Internal temperature in the winter moth.
This infrared map shows the moth's heat distribution immediately after a flight.
Red in the thorax region indicates the highest temperature.
A countercurrent heat exchanger helps maintain a high temperature in the thorax,
where the flight muscles are located, allowing the endothermic insect to fly in winter.